

LTE-M vs NB-IoT: What are the differences?
When it comes to LPWAN options for IoT businesses, two LPWAN technologies stand out: LTE-M and NB-IoT. However, it can be hard to understand the differences between these two options, making it challenging to choose between them.
In this post, we will quickly break down both LPWAN options LTE-M vs NB-IoT, so that you can make an informed connectivity decision for your IoT business.
NB-IoT
First, we're going to look at NB-IoT. NB-IoT, short for narrowband IoT, is an LPWAN technology deployed on top of mobile networks. It's best suited for indoor environments and use cases where data throughput is not a significant consideration.
Features
- No gateway required
NB-IoT doesn't require a gateway because it doesn't operate over regular LTE bands. In other LPWAN networks, an IoT device sends data to a gateway, which then sends it where it should go.
Not having a gateway reduces the barrier to entry for NB-IoT, which can be a plus for certain businesses and telecom operators.
- Focuses on low data rates
NB-IoT only supports low data rates. It's one of its key selling points, as it's one of the most efficient LPWAN options for reducing and optimising the amount of data being transferred.
- Ideal for static devices
Because it can penetrate well indoors and is optimised for low data rates, NB-IoT is ideal for devices that aren't mobile. It was designed for this purpose, and it serves this purpose very well.
Benefits
- Low cost
A major benefit of NB-IoT is its low cost. Not requiring gateways greatly reduces the cost of implementing NB-IoT.Since NB-IoT requires less infrastructure than other LPWAN technology solutions, it has very few barriers to entry.
- Suitable for use cases that don't require a high refresh rate
NB-IoT has a relatively low refresh rate, making it optimal for use cases where that isn't an issue. So, you should use NB-IoT with static sensors that need to send updated data periodically rather than constantly.
- Operates without disrupting other networks
NB-IoT doesn't interfere with other networks. It can overlap with other networks, even busy ones, without missing a beat.
This is useful for situations where multiple M2M networks operate in the same space or when IoT devices occupy a dense area, like a city.
- Supports both uplink and downlink communication
Supports both uplink and downlink communicationNB-IoT offers uplink and downlink, making it more versatile than other LPWAN solutions. This gives businesses the flexibility to set their M2M fleet up their way rather than limiting themselves to the constraint of the network.
Coverage
NB-IoT is ideal for indoor spaces thanks to its ability to penetrate walls and buildings. And since it can coexist with other networks, it works well in dense areas like cities, offices, and neighbourhoods.
Ultra narrowband
Its ultra-narrowband is the feature that allows NB-IoT to coexist with other networks without experiencing interference. It can filter out interference and noise much more than a traditional narrowband network.
LTE-M (CTA-M1)
LTE-M is another popular LPWAN technology option that offers more robust connectivity, infrastructure, and reliability thanks to being a privately managed network. This makes it more costly, so it's ideal for larger M2M enterprises.
Features
- Preferred by larger IoT enterprises
LTE-M operates on a private LTE network, which provides many benefits at a higher cost. For this reason, it's standard among larger IoT players.
- Allows higher data rates
LTE-M is designed to provide higher data rates than other LPWAN solutions, making it an ideal option for businesses that value the ability to transmit larger amounts of data at a time.
- Low latency
This network option also offers low latency, which means that data moves from and to devices fast. This feature opens up new possibilities for IoT devices that need constant, real-time connectivity.
Benefits
- Widely available in Western markets
Unlike NB-IoT, LTE-M is widely available in Western markets, including the United States. LTE-M is a must for large companies planning to deploy in this region.
- Uses the regular 4G network
LTE-M is built on regular 4G networks, providing the same support and reliability that businesses use from 4G.
- Offers the greatest bandwidth among all LPWAN technologies
This LPWAN solution has the highest bandwidth of any other LPWAN network. That makes it the best option when data throughput is a factor.
Coverage
Because LTE-M has a high bandwidth and low latency, it works well for both static and mobile devices.
Private LTE
Unlike a regular LTE network, LTE-M is a private solution. This means that IoT businesses will have access to unique features and benefits, providing a higher level of control over their IoT network.
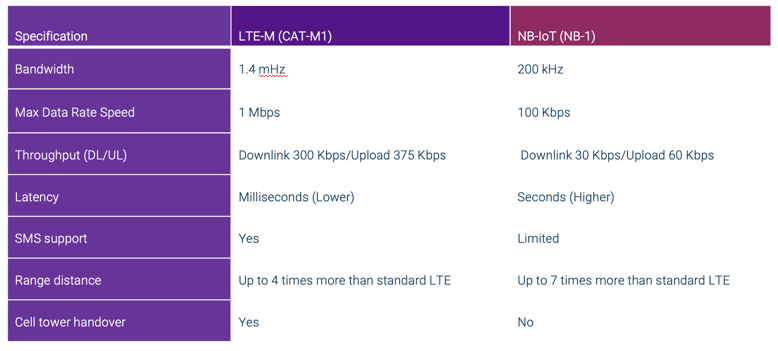
LTE-M (CAT-M1) vs NB-IoT (NB-1) Comparision Chart
Choose the LPWAN technology that's right for your business
Velos IoT offers Connect LPWA, which contains both NB-IoT and LTE-M technologies. Depending on your use cases, one might be more suitable. Contact us and find the right network technology for your unique business needs.
Want to learn more about LPWAN, its technologies and use cases, read our brief guide to low power wide area network.
Speak to a Velos IoT expert
Related articles


What Are The Differences Between LoRaWAN And NB-IoT?
When deploying and maintaining an IoT fleet, one of the most important decisions you'll make is...

Different LPWAN Technologies Explained
It's important to note that LPWAN is not a single network technology but a group of low-power wide...
